Release 2.0 of the Thermodynamics Module RUB now available
Precise determination of the properties at the operating points provides the foundation for reliable sizing and calculation in all CONVAL modules.
The Thermodynamics Module 1.0 introduced with CONVAL 6.0 enables an extremely precise calculation of the thermodynamic and transport properties of selected substances in a very wide pressure-temperature range to be taken as a sizing basis. The thermodynamic properties are derived from highly accurate equations of state, many of which are the acknowledged international standard. The transport properties are calculated using the best equations published in this field.
The new Thermodynamics Module 2.0 additionally integrates functionalities for calculating and visualizing the thermophysical properties of selected fluids.
The 64 media already supported by Release 1.0 of the Thermodynamics Module have now been augmented with nine new substances:
By specifying any combination of two property values out of temperature T, pressure p, density ρ, specific entropy s, specific enthalpy h, and steam quality, it is possible to calculate a large number of thermophysical properties as a function of the input data.
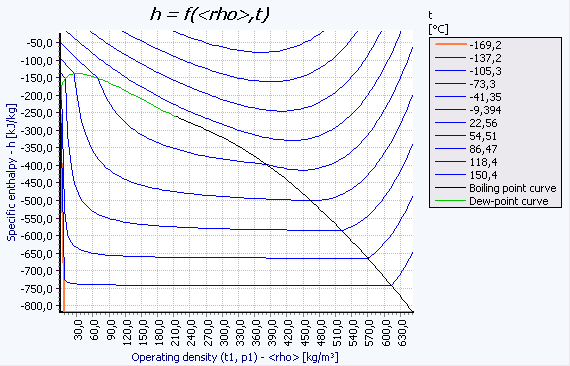
Isolines of the thermodynamic properties temperature T, pressure p, density ρ, specific enthalpy h, specific entropy s, and steam quality x can be calculated and printed out in the form of tables. All thermophysical properties included in the program module can be calculated along these isolines.
Up to 35 different phase diagrams can additionally be created for each substance.
By implementing GERG 2004, CONVAL gains access to a host of new applications, for instance in LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) projects. The AGA-8 equation so far available in CONVAL 7.0 only covers the gaseous state of a very limited spectrum of natural gas mixtures.
The GERG 2004 equation describes thermodynamic properties in the gaseous, liquid, hypercritical, and gas-liquid equilibrium states. It can be used to calculate the thermodynamic properties of gaseous and liquefied natural gases, a wide range of other compositions, and binary mixtures. The mixture calculation is integrated in all calculation modules, such as control valves. The phase equilibrium can be represented in the Thermodynamics Module as a pv(t) diagram of the mixture.
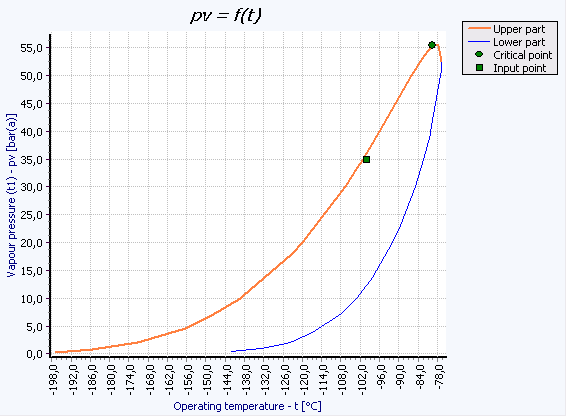
The graph above shows the phase equilibrium of a typical natural gas
For more information about GERG (European Gas Research Group), visit http://www.gerg.eu